
Blackjack Insurance: A Strategic Side Bet

Blackjack insurance is a side bet designed to safeguard against the dealer achieving a blackjack, which is a two-card 21 consisting of an ace and a 10-value card. This precautionary measure involves placing an additional bet equal to half of your initial wager. If the dealer hits blackjack, the insurance bet pays out, offsetting the loss of your original stake.
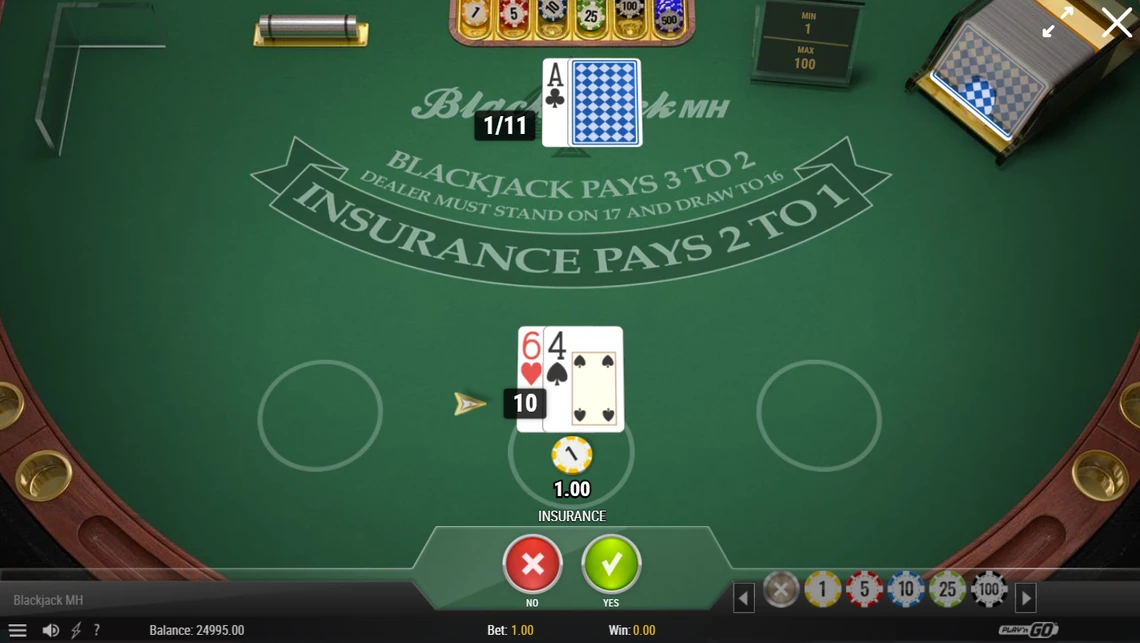
In online blackjack games, an "Insurance" button simplifies this process. When the dealer’s up card is an ace, you can quickly place the insurance bet with a single click. However, understanding when and why to use insurance is key to making informed decisions at the blackjack table.
What Is Blackjack Insurance?
The definition of Blackjack Insurance:
This is a side bet that is designed as a precautionary measure to prevent the dealer from potentially getting a blackjack, which is a hand that totals 21 with only two cards – an ace combined with a card worth 10, such as a face card.
If you opt for insurance, you will place a bet equal to half the amount of your initial bet. This allows you to recover the value of your initial bet if the dealer hits blackjack.
The Insurance button in online games :
In online blackjack games, you may see an “Insurance” button appear when the dealer’s up card is an ace. Hitting this button allows you to place the insurance bet. This feature simplifies the process, ensuring that players can make their insurance bet with one click.
How does blackjack insurance work?
To understand how “blackjack insurance” works, let’s look at the rules :
When the dealer's up card is an ace, players have the opportunity to place an insurance bet before any further action is taken. This insurance bet should be half of your initial stake. If you decide to take out insurance, you place this additional bet on the designated insurance line on the table.
The dealer will then check their face-down card to see if they land blackjack (an ace and a 10 value card):
- If the dealer has blackjack, you win twice the amount of your insurance bet. This payment helps compensate for the loss of your initial stake.
- If the dealer does not have blackjack, the insurance bet is lost, and the round proceeds as usual with your initial bet still in play.
This mechanism allows players to mitigate potential losses to the dealer's ace.
Examples :
To illustrate how "blackjack insurance" works, let's consider two examples: one where the insurance bet is won and another where it is lost.
- Example 1: Insurance Bet is Won : You place a $20 bet on a hand of blackjack. The dealer's upcard is an ace, so you decide to take insurance and place an additional $10 bet (half of your original wager) on the insurance line. The dealer then checks their hole card and reveals a 10, giving them a blackjack. Your insurance bet pays out at 2:1 odds, so you win $20 from the insurance bet (2 x $10). However, you lose your original $20 bet to the dealer's blackjack. The $20 win from the insurance bet offsets this loss, leaving you even for the round.
- Example 2: Insurance Bet is Lost : You place a $20 bet on a hand of blackjack. The dealer's upcard is an ace, and you decide to take insurance with a $10 bet. This time, when the dealer checks their hole card, they reveal a 7, so they do not have a blackjack. As a result, you lose the $10 insurance bet. The game continues with your original $20 bet still in play, and you proceed with the hand as normal. Regardless of the outcome, the $10 insurance bet is lost because the dealer did not have a blackjack.
What Are the Odds, Payout & House Edge for Insurance Bets?
Odds and Payout
Understanding the odds for insurance bets in blackjack is crucial for making informed decisions. The insurance bet costs half of your original wager and is offered when the dealer’s upcard is an ace. The payout for a winning insurance bet is 2:1, so if you bet $10 on insurance, you win $20 if the dealer lands blackjack. However, it’s important to consider the house's edge. Statistically, the dealer will land blackjack about 30.8% of the time when showing an ace, making the insurance bet generally unfavorable over the long run.
|
Aspect
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
Cost of Insurance
|
Half of the original wager
|
|
Payout for Insurance
|
2:1 (If the dealer has blackjack, you win twice the insurance bet amount)
|
|
Likelihood of Dealer Blackjack
|
Approximately 30.8% (dealer showing an ace results in blackjack about this often)
|
House edge
The house edge on insurance bets is variable and depends on the number of decks in the game: it ranges from approximately 5.8% for a single deck to 7.5% for a game with 8 decks.
|
Number of Decks
|
BlackJack Insurance House Edge
|
|---|---|
|
Single Deck
|
5.88%
|
|
2 Decks
|
6.25%
|
|
4 Decks
|
6.57%
|
|
6 Decks
|
6.67%
|
|
8 Decks
|
7.47%
|
The high house edge reflects the cost of purchasing insurance, and highlights why many seasoned players avoid this side bet.
What are the limits of blackjack insurance?
Is blackjack insurance a good bet?
When considering whether blackjack insurance is a good bet, it is important to evaluate it from a mathematical and strategic standpoint. For most players, insurance is not a good bet because it carries a high house edge, making it statistically disadvantageous over time. The insurance bet pays out at 2:1, but the probability of the dealer having blackjack is less than one-third, meaning players are more likely to lose the insurance bet than win it. This makes insurance a poor choice for those not using advanced strategies.
However, for skilled card counters who can accurately predict when the deck is rich in 10-value cards, taking insurance can occasionally be a wise move. For the average player, though, it is generally best to avoid insurance and focus on the main game.
Suitable for advanced players who have mastered card counting
The use of insurance in blackjack is primarily for advanced players who are experienced in card counting. Card counting allows the players to determine when the remaining deck has more 10-value cards, increasing the likelihood of the dealer landing blackjack. In such scenarios, taking insurance can be a strategically sound decision. But this is only valid for games with a limited number of decks. Games with a high number of decks make counting cards more uncertain.
Not recommended for beginner players
However, for the majority of players who do not count cards, it is advisable to avoid taking blackjack insurance. This is because, without precise knowledge of the card distribution, the insurance bet favors the house due to its inherent high house edge.
Advantages and disadvantages of insurance betting
|
Pros
|
Cons
|
|---|---|
|
Potential to Break Even
|
High house edge (5.88% to 7.47% depending on decks)
|
|
Useful for Card Counters
|
Low probability of dealer blackjack (<33%)
|
|
Offsets Losses if Dealer has Blackjack
|
Costly for average players not using advanced strategies
|
|
Simple to Understand and Use
|
Generally unfavorable without card counting
|
|
Adds Variety to Betting Options
|
Reduces overall expected value for non-expert players
|
Stategies & Tips
When considering blackjack insurance, here are some strategies and tips to help you make informed decisions:
- Avoid Insurance as a General Rule: For most players, it is advisable to decline the insurance bet since it carries a high house edge and is generally not profitable without specific knowledge of the deck's composition.
- Use Card Counting: If you are proficient in card counting, consider taking insurance only when the count indicates a high concentration of 10-value cards remaining in the deck. This increases the likelihood of the dealer having a blackjack.
- Basic Strategy Players: Stick to basic blackjack strategy and focus on optimizing your main hand rather than taking side bets like insurance, which can reduce your overall expected value.
- Avoid Distractions: Insurance can be tempting as a safety net, but it often distracts from the main game. Concentrate on playing your hand correctly based on the dealer’s upcard and your cards.
- Understand the Odds: Recognize that the odds of the dealer having a blackjack are less than one-third, making the insurance bet unfavorable in the long run unless specific conditions (like a high count) are met.
- Practice Discipline: Maintain discipline in your betting strategy. Resist the urge to take insurance out of fear of losing your initial bet and stick to your planned approach.
A slight variation of insurance in Blackjack: Even Money side bet
In blackjack, "even money" is a specific option offered to players when they have a natural blackjack (an ace and a 10-value card) and the dealer's upcard is an ace. This option is essentially a simplified form of insurance. Here's a detailed explanation:
What is Blackjack Even Money?
Even money is an alternative to the traditional insurance bet. When you have blackjack and the dealer's upcard is an ace, the dealer will ask if you want "even money." If you accept, you will immediately be paid 1:1 on your bet, regardless of whether the dealer has blackjack. This means you are guaranteed a payout equal to your original bet.
How Even Money Works?
- Scenario 1: You Take Even Money: You have a $20 bet and a blackjack. The dealer’s upcard is an ace. You opt for even money, and the dealer pays you $20, a 1:1 payout. You win $20 no matter what the dealer’s hole card is.
- Scenario 2: You Decline Even Money: You decide not to take even money. If the dealer does not have blackjack, you get paid the standard 3:2 for your hand, winning $30 on your $20 bet. If the dealer has blackjack, the hand is a tie (push), and you don’t win or lose any money.
Should You Take Even Money?
Taking even money is equivalent to taking insurance on your blackjack. While it guarantees a certain win, it is statistically less advantageous compared to the standard 3:2 payout you would receive for blackjack. For non-card counters, declining even money is the better option because it offers a higher expected value in the long run. However, if you prefer the certainty of an immediate win, even money can be an attractive option.
Our opinion on insurance bets in Blackjack:
While insurance in blackjack offers a way to protect against the dealer's blackjack, it generally carries a high house edge and is unfavorable for most players. Understanding the mechanics, cost, and payout of the insurance bet is essential. However, unless you are an advanced player using card counting techniques, it is best to avoid taking insurance and focus on playing your hand according to the basic blackjack strategy. By doing so, you can maximize your chances of long-term success in the game.

Author
Manager