100% Up To $2,500

Online Gambling in Michigan - Casino & Sports Betting
Michigan is one of the more advanced gambling states in the United States. You can gamble on online casinos and sportsbooks. They also allow you to gamble on horse racing and the lottery. Charitable gambling is allowed, although social gambling is illegal in the states. Our Online Gambling MI’s Guide is designed to help you find the best online gambling sites for your needs. We’ll look at what gaming options are available, the legal aspects of gambling in Michigan, how to select the best site and stay safe while doing so, and answer many more questions. We’ll offer a list of our favorite gambling sites in Michigan, as well.
Best Michigan Online Gambling Sites
-
Caesars Casino
-
BetMGM Casino
100% up to $1,000 & $25 Free Credits
-
BetRivers Casino
100% Up To $500
-
Golden Nugget Casino
100% Up To $1,000
-
Caesars Palace Online Casino
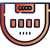
100% Up To $2,500
-
DraftKings Casino
Get Up To $1,000 Bonus Cash
-
Sports Illustrated Casino
100% Up To $1,000 & $50 Free Play
-
FanDuel Sportsbook
Bet $5, Get Up To $200
-
DraftKings Sportsbook
Bet $5, Get $150
-
BetMGM Sportsbook
Safety Net Up To $1,500
-
Caesars Sportsbook
First Bet Refund Up To $1,000
-
BetRivers Sports
First Bet Refund Up To $500
-
Sports Illustrated Sportsbook
Bet $20 & Get $200 in Free Bets
Michigan – Gambling Regulation (as of 2025)
|
Gambling Type
|
Status
|
Date of Authorization
|
|---|---|---|
|
Online Casinos
|
✅ Legal
|
December 20, 2019
|
|
Online Sports Betting
|
✅ Legal
|
December 20, 2019
|
|
Physical Casinos
|
✅ Legal
|
November 5, 1996
|
|
Horse Racing
|
✅ Legal
|
July 25, 1995
|
|
Lottery
|
✅ Legal
|
August 1, 1972
|
|
Charitable Gaming
|
✅ Legal
|
December 27, 1972
|
Michigan has developed a complete legal and operational structure for gambling, with all major categories—online casinos, sports betting, land-based casinos, horse racing, lottery, and charitable gaming—formally legalized under specific acts. The Michigan Gaming Control Board oversees licensing and enforcement across the state.
Online Casinos
Online casino gaming was legalized on December 20, 2019, when Governor Gretchen Whitmer signed House Bill 4311 into law. The Lawful Internet Gaming Act allows commercial casinos to offer online slots, table games, and poker to players aged 21 and over. The Michigan Gaming Control Board regulates all operators and platform providers.
- Status: Legal
- Date of Authorization: December 20, 2019
- Law: Act 152 of 2019 (Lawful Internet Gaming Act)
- Official Link:
https://www.michigan.gov/-/media/Project/Websites/mgcb/Internet-Gaming-and-Fantasy-Contests/ActsandRules/Lawful_Internet_Gaming_Act_PA_152_of_2019.pdf
Online Sports Betting
Online sports betting was legalized on December 20, 2019, when the Lawful Sports Betting Act (Act 149 of 2019) was signed into law. It allows licensed casinos and tribal gaming operators to offer online and mobile sports wagering to players across Michigan. The legislation was part of a broader package that expanded online gaming access.
- Status: Legal
- Date of Authorization: December 20, 2019
- Law: Act 149 of 2019 (Lawful Sports Betting Act)
- Official Link:
https://www.michigan.gov/-/media/Project/Websites/mgcb/Internet-Gaming-and-Fantasy-Contests/ActsandRules/Lawful_Sports_Betting_Act_PA_149_of_2019.pdf
Physical Casinos
Casino gambling in Michigan was legalized through Proposal E, passed by voters in 1996, and implemented through the Michigan Gaming Control and Revenue Act. This law established three commercial casinos in Detroit and provided a framework for licensing, taxation, and regulation.
- Status: Legal
- Date of Authorization: November 5, 1996
- Law: Public Act 69 of 1997 (Michigan Gaming Control and Revenue Act)
- Official Link:
https://www.legislature.mi.gov/documents/mcl/pdf/mcl-Act-69-of-1997.pdf
Horse Racing
Horse racing and pari-mutuel betting were formally regulated under the Horse Racing Law of 1995. The legislation outlines the licensing and operational requirements for live and simulcast horse racing events. The law is overseen by the Michigan Gaming Control Board.
- Status: Legal
- Date of Authorization: July 25, 1995
- Law: Act 279 of 1995 (Horse Racing Law)
- Official Link:
https://www.legislature.mi.gov/documents/mcl/pdf/mcl-Act-279-of-1995.pdf
Lottery
The Michigan Lottery was established in 1972 through the McCauley-Traxler-Law-Bowman-McNeely Lottery Act. It allows the operation of instant tickets, draw games, and participation in multi-state lotteries. The Michigan Bureau of State Lottery operates under this statutory authority.
- Status: Legal
- Date of Authorization: August 1, 1972
- Law: Public Act 239 of 1972
- Official Link:
https://www.legislature.mi.gov/documents/mcl/pdf/mcl-Act-239-of-1972.pdf
Charitable Gaming
Charitable gaming was legalized under the Traxler-McCauley-Law-Bowman-Bowman Act in 1972. The law permits eligible nonprofit organizations to conduct bingo, raffles, charity poker, and other small games of chance. Oversight is provided by the Charitable Gaming Division of the MGCB.
- Status: Legal
- Date of Authorization: December 27, 1972
- Law: Public Act 382 of 1972
- Official Link:
https://www.legislature.mi.gov/documents/mcl/pdf/mcl-Act-382-of-1972.pdf
Overall Comment
Michigan has fully legalized and professionally regulated all major forms of gambling through clear, modern legislation. It is considered one of the most advanced U.S. states in terms of legal gaming infrastructure and digital access.
Latest Michigan Online Gambling News
Explore Michigan Categories
Online Casino in Michigan
Michigan online casino is a new and exciting way to gamble. It is a great way to enjoy the thrill of gambling without having to leave your home. Live casino games are also available in Michigan. These games are played in real-time with other players from all over the world. You can play blackjack or roulette with live dealers and other players from all over the world.
Sports Betting in Michigan
The legalization of Sports Betting in Michigan has been a long time coming. The state’s voters approved the measure in November 2018, and it was signed into law by Governor Rick Snyder on December 21, 2018. The online sport betting launch took place in January 2021. This has opened up a new opportunity for bettors and sportsbooks alike.
-

-
-

-

-
 Ice Hockey
Ice Hockey -
 Golf
Golf
Conclusion on Michigan Online Gambling
Michigan is an advanced state in terms of gambling, but it continues to be on the rise in recent years. There are many online casinos or sportsbooks available with unique aspects to each one. You’re going to want to go down our checklist to find which ones work best for you.
Check the bonuses and promotions available for any online gambling site. Check reviews from reputable websites along with customer reviews to find the strengths and weaknesses of each gambling site. Consider how liquid your funds will be on each site, as well. Finally, find a site with a mobile app that you enjoy playing on, as you’ll be spending the majority of your time gambling there.
FAQs
Are online casinos legal in Michigan?
Online casinos are legal in Michigan after the Lawful Internet Gaming Act was passed in December 2019. The Lawful Internet Gaming Act was signed into law in December 2019. The next question becomes, “what is the legal gambling age in Michigan?” This depends on a couple of factors. For online gambling and as a general rule, the legal age to gamble in Michigan is 21 years of age or older.
Why should I play on legal gambling sites in Michigan?
Legal gambling sites in Michigan are required to meet a high standard administered by the state. You have a legal standing against them if anything happens, unlike illegal gambling sites.
Can you gamble online safely in Michigan?
You can gamble online in Michigan safely. Utilize legal and reputable online gambling sites.
Do online casinos pay?
Yes. In Michigan, Online casinos will payout if you win on their platform.
Will I be able to gamble in Michigan on my tablet or phone?
Yes. You can use a gambling site’s mobile website or app to gamble on your tablet or phone in Michigan.
Are live dealers available online in Michigan?
Yes. You can play several games with real live dealers in Michigan.
Can I win real money Gambling in Michigan?
Yes. You can win real money when gambling online in Michigan. All the Casinos we provide on our website pay in real money.
How can I deposit at an online casino in Michigan?
The list of deposit methods includes credit or debit cards, bank transfers, Play+ cards, PayNearMe, PayPal, Skrill, or Neteller.
Are There Legal Repercussions for Gambling Online in Michigan?
You can go to jail for illegally gambling online in Michigan, although it’s unlikely. The law states that offenses could result in up to one year in prison or a fine of up to $1,000. That’s why it’s important to play from Online Gambling Sites officially licensed in Michigan.
Am I required to download casino software to gamble online in Michigan?
You will need to download the online casino’s app to have the best mobile experience when gambling online in Michigan.
What are the best aspects to consider when looking for an online gambling site in Michigan?
You should be looking for safe gambling sites that offer great bonuses and payouts. They should have easy-to-use mobile apps with appealing designs.
Why should I download a mobile casino app?
Mobile apps are designed to easily be used on your phone or tablet, making your experience more enjoyable.
What is a Casino Operator?
A casino operator is anyone that possesses ownership in a casino.
Is there a limit to how much I can bet in Michigan?
Some gambling sites could set a limit on you depending on what you are gambling on.
Can I gamble online for free in Michigan?
Yes. You can gamble online in Michigan for free. The majority of online gambling sites offer free versions of their games.
Are online casinos trustworthy?
Yes. Legal online casinos in Michigan are trustworthy, as they are regulated by the state. Illegal or blacklisted casinos are not trustworthy options.
Can I withdraw real money?
Yes, you can withdraw real money via checks, eChecks, PayPal, Skrill, Play+ cards, or cash at the casino cage.